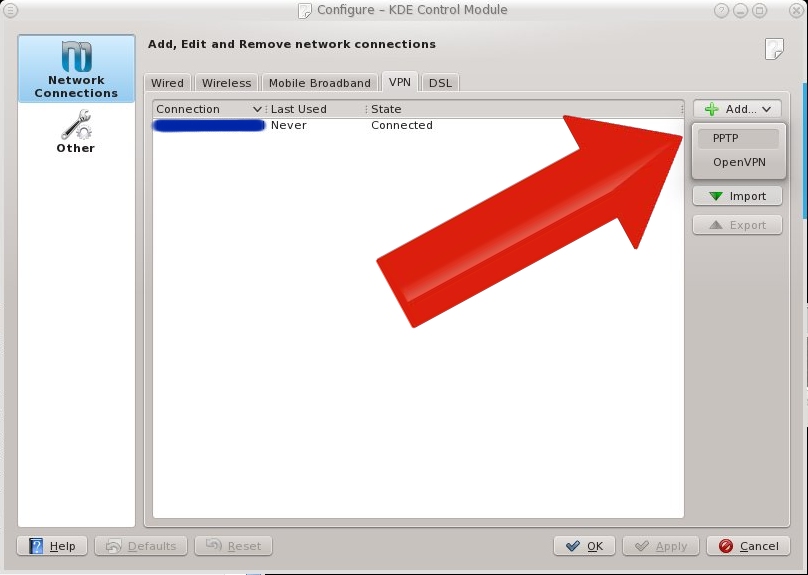
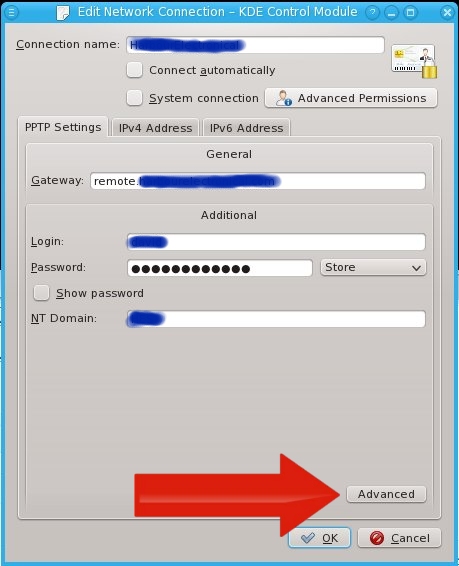
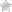In this post, I'll be writing down all steps required to build a Squid proxy server on a clean "minimal" installation of CentOS 6.0
Step 1. Network configuration
First, install system-config-network or manually configure the network. I prefer system-config-network for easy configurations and vim for more complex configurations.
yum -y install system-config-network-tui
Step 2. Install some tools for convenience
yum -y install vim-minimal vim-enhanced openssh-clients mc telnet policycoreutils policycoreutils-python bind-utils
Step 3. Install ntp and synchronize clocks
If one of the clocks it out of sync, NTLM authentication will not work. Therefore, we synchronize the clocks. Using pool.ntp.org as a source would be good, but if the AD server isn't synchronized with that source, we'd have the same problem. So I'm synchonizing the proxy to the AD server (Win2003SBS actually) instead:
rpm -q ntp || yum -y install ntp
sed -i "s/^server /#server /g" /etc/ntp.conf
echo "server AD-SERVERNAME" >> /etc/ntp.conf
ntpdate AD-SERVERNAME #synchronize right now
service ntpd start #and keep in sync
chkconfig ntpd on
Step 4. Install squid and other required software
yum -y install krb5-workstation samba-common samba-winbind authconfig squid
chkconfig squid on
Step 5. Connect to active directory
Please note that MYCOMPANY.local and mycompany.local may be different domains due to the upper/lowercase.
ADSERVER=sbs.MYCOMPANY.local
DOMAIN=MYCOMPANY.local
WORKGROUP=MYCOMPANY
authconfig --enableshadow --enablemd5 --passalgo=md5 --krb5kdc=$ADSERVER \
--krb5realm=$DOMAIN --smbservers=$ADSERVER --smbworkgroup=$WORKGROUP \
--enablewinbind --enablewinbindauth --smbsecurity=ads --smbrealm=$DOMAIN \
--smbidmapuid="16777216-33554431" --smbidmapgid="16777216-33554431" --winbindseparator="+" \
--winbindtemplateshell="/bin/false" --enablewinbindusedefaultdomain --disablewinbindoffline \
--winbindjoin=Administrator --disablewins --disablecache --enablelocauthorize --updateall
service winbind restart
chkconfig winbind on
Give squid permissions to use winbind info:
usermod -G wbpriv squid
Now check your winbind connection using the following commands:
wbinfo -u
wbinfo -g
Step 6. Firewall
iptables -I INPUT -m tcp -p tcp --dport 3128 -j ACCEPT
/sbin/service iptables save
Step 7. Configure squid
I commented out this line from /etc/squid/squid.conf:
http_access allow localnet
That line would have allowed users from 10.0.0.0/8+172.16.0.0/12+192.168.0.0/16 and others to use the proxy without authentication. Then I added the following right below that line:
acl whitelist dstdom_regex -i "/etc/squid/whitelist"
http_access allow whitelist
auth_param ntlm program /usr/bin/ntlm_auth --helper-protocol=squid-2.5-ntlmssp
auth_param ntlm children 5
auth_param ntlm keep_alive on
acl our_networks src 192.168.0.0/16
acl ntlm proxy_auth REQUIRED
http_access allow our_networks ntlm
authenticate_ip_ttl 900 seconds
This will allow all valid, logged in users to surf the web. You could also limit which users can surf by adding --require-membership-of=ADGROUPNAME to the ntlm_auth command
The first two lines of above configuration point to a file /etc/squid/whitelist. This file contains domains that should never be denied. My whitelist file contains:
\.trendmicro\.com
^trendmicro\.com
\.microsoft\.com
^microsoft\.com
This means that anything at *.microsoft.com and microsoft.com (without subdomain) as well as *.trendmicro.com as trendmicro.com (my virusscanner) is always allowed for any user. We wouldn't want to block important updates.
Start Squid using /sbin/service squid restart and the proxy is ready.
Step 8. Optional: IPv6 issues
I've been experimenting with IPv6 for a while now, but I don't have IPv6 available on all systems. That caused me some trouble with the next step. I had to give preference to IPv4 above IPv6 by editting /etc/gai.conf:
label ::1/128 0
label ::/0 1
label 2002::/16 2
label ::/96 3
label ::ffff:0:0/96 4
label fec0::/10 5
label fc00::/7 6
precedence ::ffff:0:0/96 100
precedence ::1/128 50
precedence ::/0 40
precedence 2002::/16 30
precedence ::/96 20
Step 9. Optional: Some white- and blacklisting
We may not want to allow all sites to be visited. For instance, porn sites are often blocked in office situations. I've got a manual on blacklisting using SquidGuard as well.
© GeekLabInfo Squid with active directory authentication on Centos 6.0 is a post from GeekLab.info. You are free to copy materials from GeekLab.info, but you are required to link back to http://www.geeklab.info



 (2 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
(2 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
 Loading...
Loading...